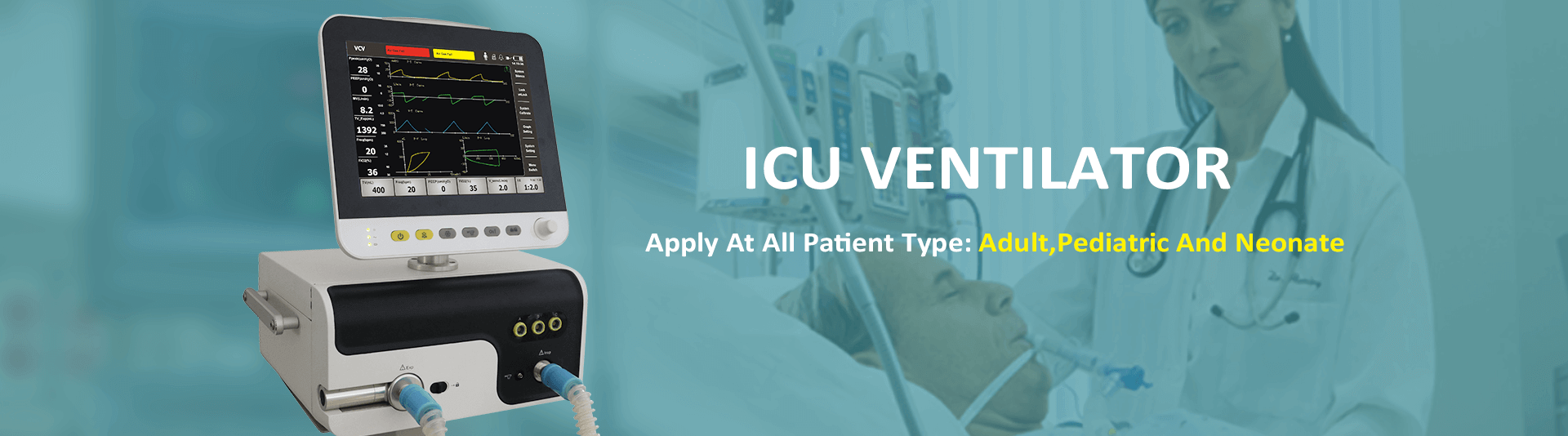
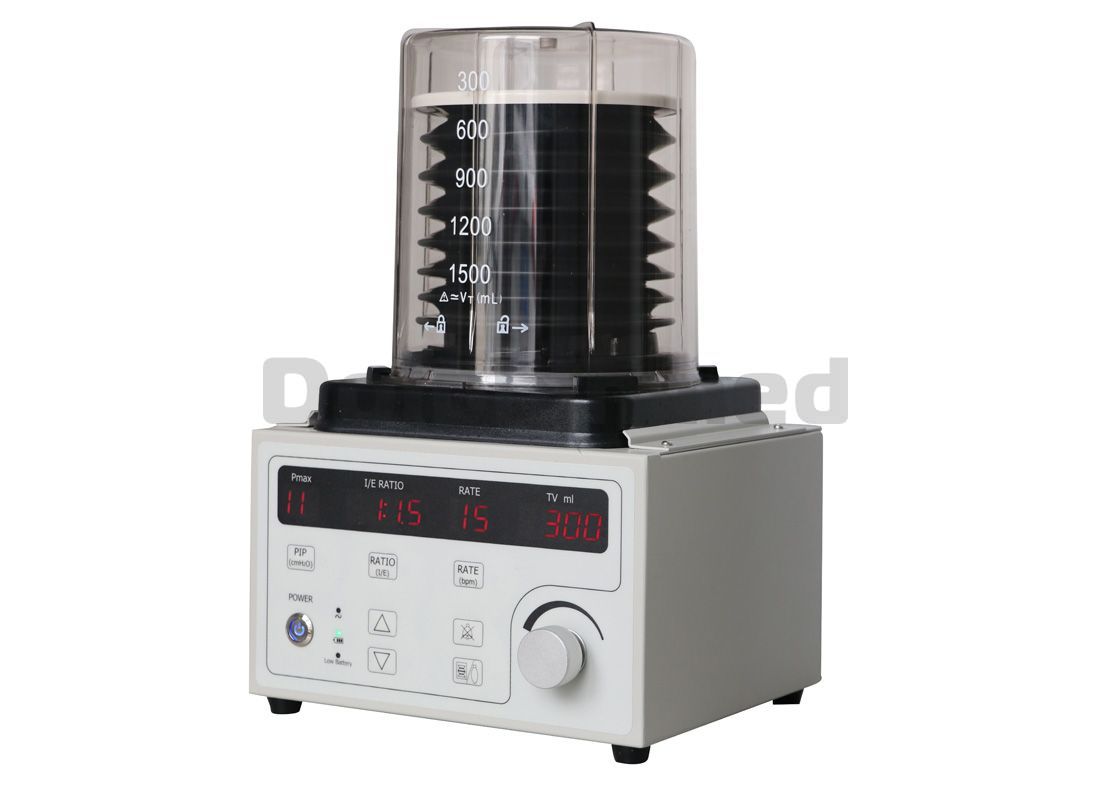
What Is The Working Principle And Advantages Of Medical Anesthesia Ventilator?
The Medical Anesthesia Ventilator has a typical time conversion feature and is typically powered by a motor or compressed gas. Recently, the anesthesia machine produced abroad has a built-in electric electronically controlled ventilator, which does not need to drive the gas. It can be ventilated by the atmosphere in case of gas failure to ensure patient safety. In a typical ventilator, the bellows is attached to an anesthetic breathing circuit and placed in a clean plastic chamber containing anesthetic gas. During exhalation, the drive gas is delivered into the chamber to compress the bellows. O2 is used as the driving gas in the bellows, and the concentration of O2 inhalation is easy to increase. During exhalation, the driving air is discharged into the room, and when the patient passively inhales, the bellows is refilled. The Hospital Ventilator Machine can also be dangerous. Common risk factors are: the anesthesia loop is not connected or connected to the patient; the delivery pressure is too high; the ventilator exhaust valve is faulty; the drive mechanism is faulty. The anesthesia loop anesthesia loop is between the anesthesia machine and the common gas outlet. The anesthesia loop functions to deliver anesthetic gas and oxygen to the patient and expel CO2. The loop system includes fresh gas inlets, inspiratory and expiratory singles, inhalation and exhalation ribs, Y-joints, adjustable exhaust, mediation, and CO2 absorbers.







 English
English  French
French  Chinese
Chinese  Spanish
Spanish