Do you know the classification of the ventilator?
In modern clinical medicine, the Mechanical Ventilator Machine, as an effective means to artificially replace the autonomous ventilation function has been widely used in respiratory failure caused by various reasons, anesthesia breathing management during major surgery, respiratory support treatment and emergency resuscitation, Occupy a very important position in the field of modern medicine. The ventilator is a vital medical device that can prevent and treat respiratory failure, reduce complications, save and extend the life of patients. As a Hospital Ventilator Machine Exporter, let me introduce you.
fIrst. Classified by type of use or application
CMV 1. Definition: When the patient's spontaneous breathing weakens or disappears, the patient's breathing is generated, controlled, and regulated entirely by a mechanical ventilator. 2. Application: The spontaneous breathing disappears or weakens due to the disease; when spontaneous breathing is irregular or the frequency is too fast, and mechanical ventilation cannot be coordinated with the patient, the spontaneous breathing is artificially suppressed or reduced.
AMV 1. Definition: In the presence of patient breathing, the ventilator assists or enhances the patient's spontaneous breathing. The various types of mechanical ventilation are mainly triggered by the patient's inspiratory negative pressure or inspiratory airflow. 2. Application: Although spontaneous breathing exists and is more regular, patients with spontaneous breathing weakened and insufficient ventilation.
Second. Classified by use of mechanical ventilation
Intrathoracic or airway compression
Chest shape
Third. Classification by switching between inhalation and exhalation.
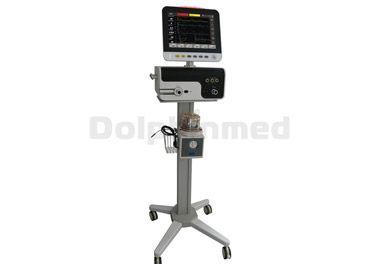
Hospital Ventilator Machine
1. Constant pressure: After the pressure in the airway reaches the expected value, the ventilator opens the exhalation valve, and the thoracic and lungs passively collapse or exhale due to negative pressure. When the pressure in the airway continues to drop, the ventilator generates again with positive pressure. Airflow and cause inhalation.
2. Constant volume type: The expected tidal volume is sent into the lungs by positive pressure. When the estimated tidal volume is reached, the air supply is stopped and the state of expiration is entered.
3. Timing type: Supply air according to pre-designed inspiratory and expiratory time.
Fourth. Supply air at the ventilation frequency
High-frequency ventilation: ventilation frequency> 60 times / minute.
1. Advantages: low airway pressure, low intrathoracic pressure, little interference to the circulation, no need to close the airway.
2. Disadvantages: Not conducive to the removal of carbon dioxide.
3. Classification: high-frequency positive pressure ventilation, high-frequency jet ventilation, high-frequency oscillating ventilation.
2. Normal frequency ventilation: ventilation frequency <60 times / minute.
Fifth. Classified by sync device or performance
1. Synchronous ventilator: When the patient's spontaneous breathing starts, the ventilator can be triggered to supply air to the patient's respiratory tract and produce an inspiratory action.
2. Non-synchronized ventilator: The patient's breathing or inspiratory negative pressure cannot trigger the ventilator to supply air, and is generally only used for patients with controlled mechanical ventilation.
Sixth. Classified by applicable objects
Baby ventilator
Infant ventilator
Adult ventilator
Seventh. Classified by working principle
Simple ventilator
Membrane lung
Our company also has Hospital Ventilator Machine on sale, welcome to consult.






 English
English  French
French  Chinese
Chinese  Spanish
Spanish